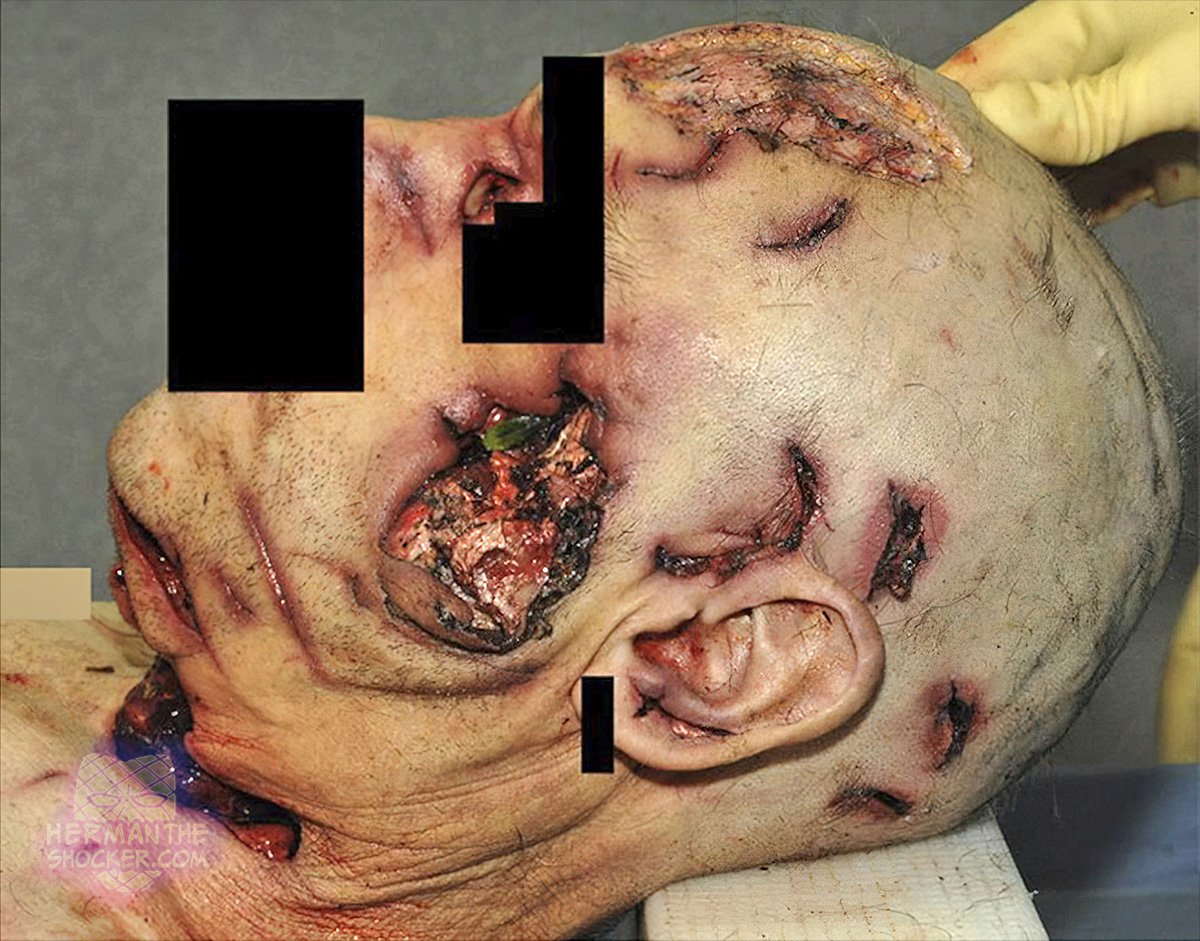
Australia. This middle aged adult male has blunt- and sharp-force trauma injuries to the head and neck after getting fatally assaulted by an unknown person in a park. There was no info about the perpetrator.
There were a number of lacerations on multiple surfaces of the head including the face, predominantly on the left side. There were multiple blunt-force injuries to the head associated with depressed skull fractures of the frontal and temporal bones. On reflection of the scalp, there was a small amount of subgaleal hematoma associated with the scalp lacerations. There was an inverted domed, circular depressed fracture of the right frontal bone. On the left frontal bone was a depressed triangular-shaped fracture with corresponding overlying laceration. Located posterior and slightly superior to this is a similar, vaguely triangular-shaped depressed fracture and a small linear fracture extended between these two fractures.
On examination of the inside of the skull, there was extensive comminuted fracturing of the left temporal bone and middle cranial fossa. This extended into the petrous-temporal bone. The posterior component of the temporal fracture had a circular profile. This was associated with laceration of the overlying dura. There were small linear fractures of the roof of the left orbit. There was no significant extradural or subdural hemorrhage. There was patchy subarachnoid hemorrhage about the brain.
There was blunt-force injury to the face associated with extensive fractures of the left maxilla, zygoma, and nasal bones. Across the front of the neck, there was a complex 120 mm incised wound, which extended across the front of the neck. The right end of the wound was an area of tailing abrasion, which extended into a superficial incised wound. The larger wound transected the trachea and blood vessels within the neck. The laryngeal skeleton was intact.
This injury was also associated with grooving of the body of the 6th cervical vertebra. There was also a linear fracture of the inferior aspect on the body of the mandible on the left side. There were multiple parallel linear abrasions over the left anterior chest wall. There was a fracture of the posterior right 11th rib associated with bruising of the overlying skin. There were incised/chopping injuries to the left elbow, right wrist, right distal upper arm, and anterior left shoulder. There was a superficial stab injury to the front of the left shoulder. There was bruising and abrasion about both wrists. There was a gouging-type injury to the left index finger fingernail. There was also evidence of postmortem insect activity and animal scavenging.
The individual had a number of different injuries. These included chopping-type injuries to the lower face. Chopping injuries are caused by a blow with a firm implement with a thin and variably sharp edge, such as an axe or machete, and show features of mixed blunt- and sharp-force injury. A sharp-bladed implement caused the injury to the front of the neck. There were at least 10 discrete blunt-force injuries to the head and face, a number of which may have been caused by an implement with a rounded domed surface.
There were linear abrasions over the left chest wall that showed characteristics of being inflicted by a blunt implement with a thin edge. The absence of lacerations suggests these wounds may have been inflicted through clothing. There was a superficial stabbing injury to the front of the left shoulder. There were sharp force injuries to the left elbow, back of the right wrist, and just above the outer aspect of the right elbow. These were nonspecific but may represent defensive injuries.
Postmortem CT showed multiple well-defined fractures of the skull vault including the central frontal bone, where there is a rounded, centrally depressed circular fracture and two semicircular (one curved and one circular edged) depressed fractures of the left frontal bone. There were grossly comminuted fractures of the nasal bones and left orbit, maxilla, and mandibular condyle extending into the left squamous temporal bone. There were separate linear fractures of the inferior aspect of the anterior mandibular body. There was a further separate rounded depressed fracture of the left parietal bone at the posterior aspect of the squamous temporal fractures. CT also showed a fracture to the posterior aspect of the right 11th rib.
Latest posts