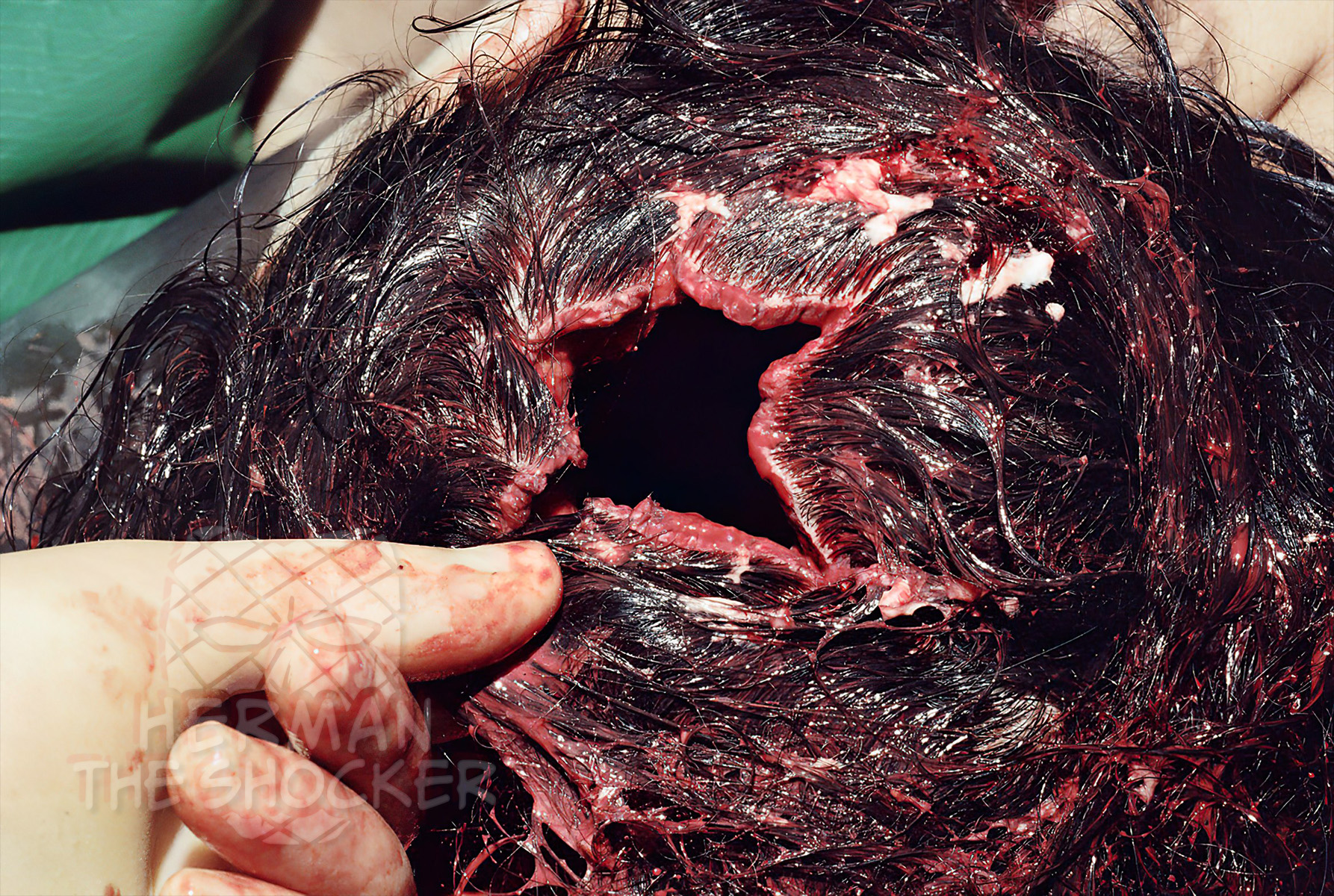
Initially, it may be difficult to distinguish the entrance and exit wounds, but by loosely reconstructing the skull and the wound edges, the injuries can be seen. In this case an exit wound. Despite the extreme amount of cranial destruction, careful and meticulous reapproximation (bring separated parts back together) of the calvarium, scalp, and tears allows for the demonstration and confirmation of an exit wound. Reconstruction of the wound can be very important to determine particular wound characteristics in cases of alleged homicide.
Head injuries from shotguns are typically quite devastating, often with extensive soft tissue destruction, skull fractures, and pulpifaction of the brain. Occasionally, the brain is largely expelled from the cranial vault and may be found near the body.
Latest posts