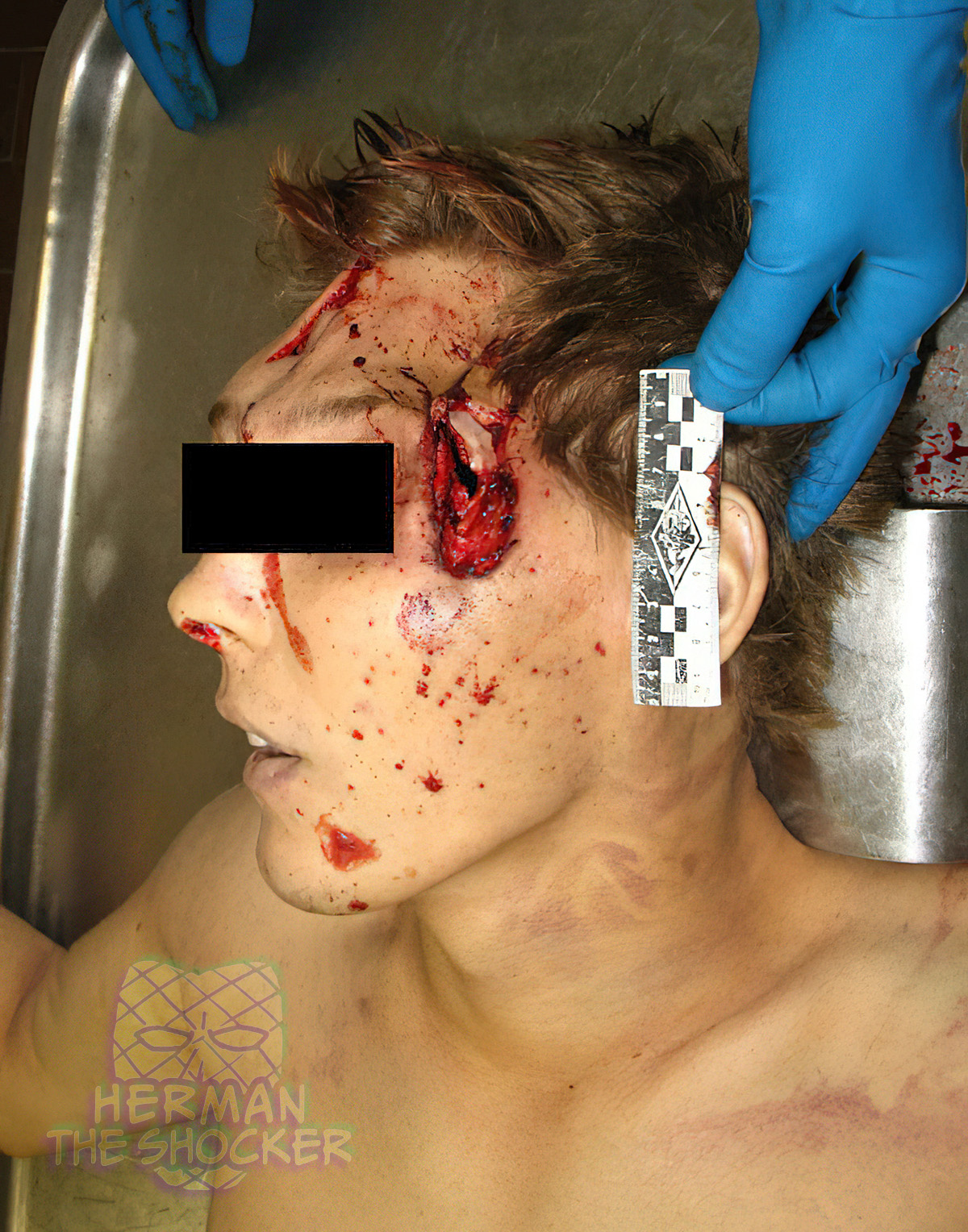
This individual committed suicide by shooting himself in the head with a hunting rifle, no further info on this case.
Head injuries from shotguns and high-powered rifles are typically quite devastating, often with extensive soft tissue destruction, skull fractures, and pulpifaction of the brain. Occasionally, the brain is largely expelled from the cranial vault and may be found near the body. Self-inflicted submental and transoral wounds may produce serious but survivable brain injuries if the path of the bullet is limited to the frontal area.
Centerfire rifles, whether military or hunting, frequently cause a strong ‘explosive’ effect with comminution of bones and laceration of brain tissue up to a so-called Kröhnlein shot (exenteratio cranii). Shotgun injuries differ substantially depending on the range of fire. Close-range shots have a tremendous effect similar to centerfire rifles by literally riddling brain tissue and blasting the skull. The high internal cranial pressure often leads to long skin tears, also detached from the bullet opening, as well as extensive bone fracture systems and brain tissue destruction.
The head is the most common location for a suicidal shotgun wound (74%), followed by the chest (20%) and then the abdomen (6%). In head wounds, the most common location was intraoral (50%), followed by under the chin (19%); side of head, including parietal and temporal wounds (15%); and the face, including the forehead (13%).
Latest posts